Rh- Negative Mother & Pregnancy
You're Rh-Negative & Pregnant...now what?
Congratulations on your baby!!
Now that you know you are pregnant, your doctor should be checking your blood for the Rh-negative (Rh-) Factor. So what does this mean and why does it matter?
There are 8 main blood types in human beings. The Rh-positive types are A, B, AB and O. The Rh-negative blood types are A-, B-, AB- and O-. The Rh-negative (Rh-) Factor is much more rare than the Rh-positive (Rh+) Factor, accounted for only 15% of the US Population. When you are Rh-negative it means that you do not have a protein called, The Rh Factor, named for the Rhesus Monkey protein or the D antigen, on the surface of your red blood cells. Blood Type & Factor play an important role in pregnancy when an Rh-negative (Rh-) woman becomes pregnant with a man who is Rh-positive (Rh+). Since 85% of the US Population is Rh-positive (Rh+), it stands to reason that Rh-negative women are more likely to get pregnant by an Rh-positive mate. For more on the Migration and Distribution of the Rh- Factor Blood Line, please click here.
There are reasons why your doctor will test your blood during your pregnancy. However, finding out your blood type and the compatibility of your mates is the most important. If you are pregnant and Rh-negative and are carrying a child that is Rh-positive, like the child's father; your baby and future pregnancies can be at risk for a serious medical disease, birth defect or worse miscarriage and death.
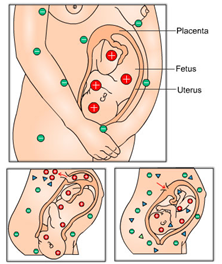
When an Rh-negative mother is exposed to her Rh-positive baby's blood, the mother's body is at risk for becoming "sensitized". This causes the mother's immune system to shift into gear and begin producing antibodies that are specifically designed to find and destroy these foreign blood cells.
During your first pregnancy, these antibodies are typically not dangerous, because chances are that you will not be exposed to your child's blood until delivery. Therefore, the first child would typically be unaffected. However, once an Rh-negative mother has been exposed or sensitized to her child's Rh-positive blood, the process of building a multiplying army of antibodies has began. These antibodies will sit in wait for the next pregnancy and once the Rh-positive cells are recognized, the antibodies are programmed to attack. Without medical intervention, all of your subsequent pregnancies are at risk of being self terminated by these antibodies.
In the late 1940's the Rh-negative factor was discovered by two scientists, who began looking for a cure to a disease that killed 2 dozen babies each day. In 1968, a process of medical intervention was invented and a product called RhoGAM or (Brand Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human), became FDA approved and available for use. When an Rh-negative mother is given an "injection" of RhoGAM, it protects her immune system from being exposed to the Rh-positive blood. RhoGAM is usually administered twice during your pregnancy, if you choose to get it, once at 28 weeks and again within 72 hours of delivery. RhoGAM is a human blood/plasma product. If you would like to find out more about RhoGAM's donor, screening and/or manufacturing process, please  click here to be redirected to the
click here to be redirected to the  Johnson & Johnson Company, RhoGAM Homepage.
Johnson & Johnson Company, RhoGAM Homepage.
Since 1968, other competitive products have also become available for use in this situation. Please do your own research on the positive and negative effects, risks and ingredients of each drug, so that you can make the most informed decision on how to handle your bodies Rh- Pregnancy.
Without use of Medical Intervention, the immune system of an Rh-negative mother will not be controlled. These sensitized antibodies it has created are from the first pregnancy are specifically programmed, ready and waiting to attack the Rh-positive (Rh+) blood cells of your subsequent pregnancies. As the antibodies begin to attack and destroy the red blood cells of your pregnancy, it can lead to serious complications including Anemia, Jaundice, Cerebral Palsy, Mental Retardation, Heart Failure and even death in severe cases. This horrible condition is called Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn or HDN and in severe cases would typically cause a still birth or cause death very shortly after birth.
In General, for the protection of your future pregnancies, all Rh-negative woman should be treated for Rh-positive sensitization after a normal delivery, a miscarriage, an induced abortion or menstrual extraction, an ectopic pregnancy, chorionic villus sampling, external cephalic version, amniocentesis, hemorrhage, abdominal trauma, still birth, fetal blood sampling and any blood or plasma transfusions.
There are some doctors, who will tell those people with Rh-negative, that their blood type causes no special health concerns; except when they give or receive blood, or during pregnancy. However, THIS IS NOT TRUE. There are other Medical and Genetic Issues that are associated with being a person who has Rh-negative (Rh-) blood. For more information on Medical and Scientific Research and Studies related to the Rh- Factor, please click here.
If you are an Rh- Mom, please take a moment to think about your children.
There is a chance that you may have passed your Rare Rh- Blood Type on to your children.
Protect their future by knowing where you can find a matching rare blood type donor quickly!
to the Rh-Negative Registry
For Only $1.99
Th meg question
May 23, 1976Ms
May 23, 1976Need help
May 23, 1976Helo
May 22, 1976This is a story about how the lack of education can
lead to questioned paternity, even in this day and age...
The father of a newborn tells us this tale about how he "could have" questioned whether the baby was his or not, because of something a midwife says regarding the newborns rhesus status. Enjoy his story!
The day after the birth, while we are both lying on our bed, very tired, a midwife comes by and asks us whether we know the rhesus status of the baby. We answer negatively, she checks her notes and says, “Ah, good news, the baby is rhesus negative. The father must also be rhesus negative then!” Well, he says, I am not…
 Click here to continue reading this story about the rhesus factor and midwives that make random comments about genetics. The father says, "maybe they should know better before making any comments that are not required. He also states, "I can imagine that a statement of this type could make a father quite suspicious for no good reason," had he not known better!
Click here to continue reading this story about the rhesus factor and midwives that make random comments about genetics. The father says, "maybe they should know better before making any comments that are not required. He also states, "I can imagine that a statement of this type could make a father quite suspicious for no good reason," had he not known better!
This is a good example of how undereducated even professionals can be when discussing something like the Rhesus Factor; that effects only a small percentage of the total population. We individually need to make ourselves more aware of the facts, become more proactive and ask more questions!
How did you get your Rh-Negative Blood Type?

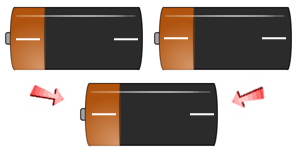
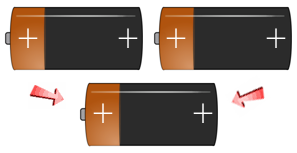
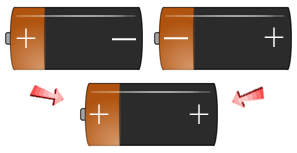
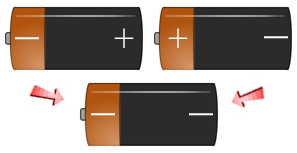
Every human being is born with two (2) individual Positive or Negative Rh Blood Factors. During conception, each parent must pass one (1) of their "Factors" on to their children. Below you can see the way a child's Positive or Negative Rh Blood Factor is finally determined; based on their receipt of the two parents combined Rh Factors.
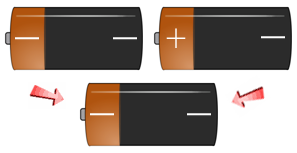
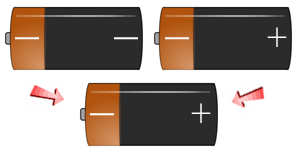
- If a person has + + genes, they are Rh-positive (Rh+).
- If a person has + - genes, they are Rh-positive (Rh+).
- If a person has - - genes, they are Rh-negative (Rh-).
Use the battery slide show image examples below to get an understanding of the different ways the Rh-positive and Rh- Negative Factors are passed down to your children. If you have an Rh-Negative Parent - You are Rh+/- , you have a recessive Rh Negative Factor and will be classified as Rh+.
So is there ever an exception?
Can two Rh- parents ever have an Rh+ child?
The answer to this really important question is yes. And the answer is for a much simpler reason than the blue-eyed parents having a child with green eyes that we discuss in our answer  here.
here.
The reason is that people who test negative for Rh aren’t always Rh-. The test isn’t always sensitive enough to get the right answer (although it usually does). And it only tests for one of the two Rh genes. And it doesn’t test for any of the other genes that can cause similar problems.
To understand how the test could go wrong, we first need to dig a bit deeper into Rh biology and our immune system.
Rh status is usually explained as this simple, one gene trait.
But there are two Rh genes, RhD and RhCE. There are also other genes with names like Kell, Duffy and Kidd that can cause similar problems.
Read more,  click here>
click here>
What is the Importance?
Read more about why it matters
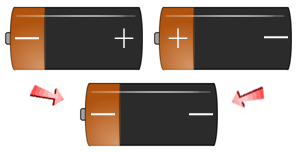
Two Rh+ people CAN have an
Rh- baby if BOTH parents carry the
RECESSIVE Rh-Negative Factor!
If you are an Rh-Negative Mother carrying an Rh- Negative Child, conceived by an Rh-Negative Father; You do not need a RhoGAM injection.
In the US, we promote the shot for all pregnancies and sometimes it is just not necessary. Please, take the time to do your own research before making your treatment decision.
The information below has been gathered together to create a well rounded starting place for you to begin your personal research.
Anti-D (Rho) Immunoglobulin: USA
RhoGAM -  Visit RhoGAM Home Page
Visit RhoGAM Home Page
Miscellaneous Facts & Concerns
- RhoGAM is a Human Blood Product, created by a donor pool of 300+ people.
- You can get a Mercury Free RhoGAM injection
- The FDA took Thermerosol out of Rhogam in 2001. This was the ingredient in the shot that contained mercury.
- The shot was originally given within 72 hours of birth. Now it is common for it to be given routinely during pregnancy around 28 weeks
- Autism, Developmental delays, cerebral palsy, mild retardation, and epilepsy connection concerns.
- PUPPPS (a burning, itching rash all over the body) from this shot.
- You may be told that you have to get the RhoGAM injection or your children could die at delivery.
Australian doctors reportedly used pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) to screen embryos for their blood group, to ensure that the embryo selected for implantation shared a rhesus negative blood group with the mother ( BBC news report).
BBC news report).
 KamRho-D IM
KamRho-D IM
Product Type: (Human Anti-D (Rho) immunoglobulin)
 US Patent 7276236
US Patent 7276236
Anti-D (Rho) Immunoglobulin: UK
- D-GAM ® (Bio Products Laboratory)
- Partobulin SDF ® (Baxter Bioscience)
- Rhophylac ® (ZLB Behring)
- WinRho SDF ® (Cangene Corporation)